GitLab Integration
CI/CD workflow
Don't hesitate to reach out if you need assistance on CI/CD, from workflow definition to actual setup in your version control system, we are here to help.
Workflow
This example demonstrates how to integrate lgc in GitLab with a classic 3-stages workflow (template down below).
CI/CD variables
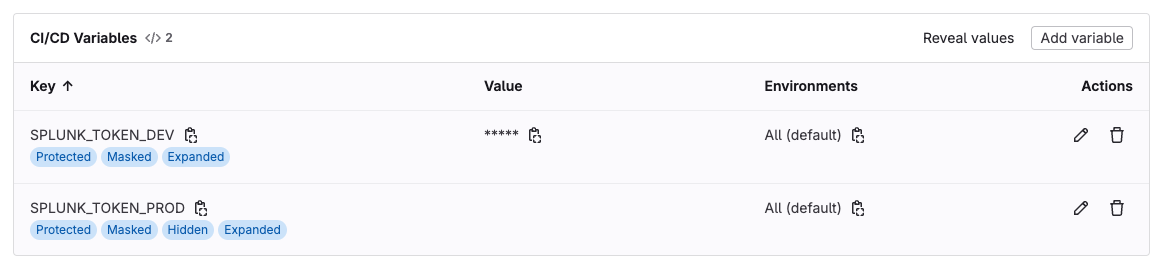
The first step to integrate lgc with GitLab is to define secrets, token and credentials as GitLab CI/CD variables. While this is optional, this is highly advised for security reasons (do not store/commit credentials in a repository).
Go to your project's Settings, under CI/CD > Variables you should be able to create CI/CD variables. In this example, 2 CI/CD variables are created: SPLUNK_TOKEN_DEV and SPLUNK_TOKEN_PROD.
Flag 'protect variable'
When creating a new variable, GitLab activates the flag 'Protect variable' by default to "export variable to pipelines running on protected branches and tags only". This setting needs to be turned off if lgc needs to work from unprotected branches.
Now, adjust lgc.toml to reference these variables:
...
[services.splunk-prod.settings]
auth_type = "Bearer"
token = "${SPLUNK_TOKEN_PROD}"
...State file
In order for your team to not step on each other toes, lgc state file must be stored using GitLab state management service. This provides, in addition to access management, versioning, and encryption out of the box.
Edit lgc.toml as follow:
[state]
type = "http"TIP
While more options exists in the [state] block, the recommended approach is to keep lgc.toml as minimal as possible and to define the state configuration in .gitlab-ci.yml.
Now, create the file .gitlab-ci.yml at the root of the repository and define variables according the following example to setup the http state backend.
variables:
# Default target environment is dev
LGC_IDENTIFIER: dev
# Use Gitlab state store
LGC_STATE_ADDRESS: ${CI_API_V4_URL}/projects/${CI_PROJECT_ID}/terraform/state/${LGC_IDENTIFIER}
LGC_STATE_USERNAME: gitlab-ci-token
LGC_STATE_PASSWORD: ${CI_JOB_TOKEN}
LGC_STATE_LOCK_ADDRESS: ${LGC_STATE_ADDRESS}/lock
LGC_STATE_LOCK_METHOD: POST
LGC_STATE_UNLOCK_ADDRESS: ${LGC_STATE_ADDRESS}/lock
LGC_STATE_UNLOCK_METHOD: DELETEDetails
At this point, if you need to run lgc locally, export the environment variables, for example LGC_STATE_ADDRESS=test lgc validate.
GitLab configuration
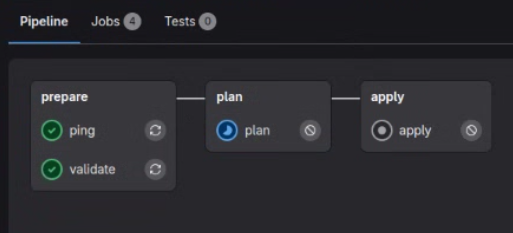
The following GitLab CI/CD configuration file .gitlab-ci.yml defines 3 stages:
- The preparation stage where lgc ensures remote systems are reachable and security detections are correctly formatted (linted)
- If the previous stage is successful, lgc plan runs to display the actual changes between the desired state (detection files in the repository) and the actual state (what is currently running)
- Finally, lgc apply is executed, either in a fully automated manner, either after a human being validates the action in the GitLab interface, depending on the target environment.
This example assumes a production and a development environment.
| Env. | What triggers the workflow | Deployment |
|---|---|---|
dev | merge request or a commit into an existing merge request | Fully automated |
prod | merge or a commit to the main branch | Human validation |
variables:
# Console colors
LGC_FORCE_COLORS: "true"
# Configure LGC to use GitLab state store.
LGC_STATE_ADDRESS: "${CI_API_V4_URL}/projects/${CI_PROJECT_ID}/terraform/state/${LGC_IDENTIFIER}"
LGC_STATE_USERNAME: "gitlab-ci-token"
LGC_STATE_PASSWORD: "${CI_JOB_TOKEN}"
LGC_STATE_LOCK_ADDRESS: "${LGC_STATE_ADDRESS}/lock"
LGC_STATE_LOCK_METHOD: "POST"
LGC_STATE_UNLOCK_ADDRESS: "${LGC_STATE_ADDRESS}/lock"
LGC_STATE_UNLOCK_METHOD: "DELETE"
# LGC_IDENTIFIER defaults to dev.
LGC_IDENTIFIER: "dev"
# Rules per environment (dev, prod).
.env_rules: &env_rules
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == 'merge_request_event'
- if: $CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH
variables:
LGC_IDENTIFIER: "prod"
image:
name: "ghcr.io/logcraftio/logcraft-cli:latest"
stages:
- prepare
- plan
- apply
validate:
stage: prepare
script:
- lgc validate
rules: *env_rules
ping:
stage: prepare
script:
- lgc ping $LGC_IDENTIFIER
rules: *env_rules
plan:
stage: plan
script:
- lgc plan $LGC_IDENTIFIER --verbose
rules: *env_rules
resource_group: "${LGC_IDENTIFIER}"
environment:
name: $LGC_IDENTIFIER
action: prepare
apply:
stage: apply
script:
- lgc apply $LGC_IDENTIFIER --auto-approve
rules:
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event"'
# Override the default rule to enforce manual approval for prod.
- if: "$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH"
when: manual
variables:
LGC_IDENTIFIER: "prod"
resource_group: "${LGC_IDENTIFIER}"
environment:
name: $LGC_IDENTIFIER
action: start